
S 400 TRIUMF: Transforming India’s Air Defence
Tue, 01 Jun 2021 | Reading Time: 7 minutes

“The Russian S-400 is arguably one of the very best all-round strategic SAM systems in operation today”
STRATFOR Worldview
An Air Defence (AD) System, as the name implies, is a weapon system designed and equipped to deter, thwart and defeat an aerial threat. Further adapting this definition to the modern AD systems globally in vogue/ being fielded, an Integrated AD System (IADS) or key components thereof, must incorporate real time surveillance, weapon control and task management systems that can survive and operate in a harsh and hostile battlefield environment.
Establishment of Necessity and Overview
With a disproportionate increase in the quality and manifestation of aerial threats, there was an imperative and urgent need to acquire an AD system capable of thwarting such threats in the Tactical Battle Area and at longer ranges simultaneously. The Russian S-400 Triumf AD System snugly fits this bill! As a lay example, a S-400 System deployed outside New Delhi would be able to track a Pakistani fighter aircraft immediately after take-off from Sargodha Air Base, near Lahore and engage it as it crosses the International Border. A similar capability to track/ engage aerial targets fielded by China from certain locations the Tibetan Autonomous Region would also exist.
The S-400 Triumf (translated as Triumph) ( NATO Code Name: SA 21 Growler) is an AD system developed by Russia’s Almaz Central Design Bureau, a Soviet/ Russian Military R & D enterprise. The S-400 has been in service since 1999 and is in use in China (China was the first country to sign a Government to Government contract with Russia in 2014 for delivery of two Regiments, completed in July 2019) and Turkey, with contractual processes underway/ finalized for India, Belarus, Saudi Arabia and some North African countries.

Development
The development of the S-400 began in the late 1980s/ early 1990s, during the closing years of the Cold War. The Russian Air Force initially announced the S-400 System in 1993. Budget restrictions following the collapse of the Soviet Union limited Russia’s ability to design an entirely new AD system. Apropos, nearly 80% of the technology for the S-400 has been adapted from the erstwhile S-300 Long Range Surface to Air Missile (LR SAM) AD System, which includes the missile containers, launchers and radars. However, vastly enhanced target tracking/ engagement ranges and increased target engagement profile make the S-400 a far more potent AD system.
The system was approved for service in 2007 and in July the same year, succeeded in destroying two simulated targets flying at Mach 8 (approximately 2700 m/s), at an altitude of 16km. The first S-400 System was inducted for operational deployment near Moscow in August 2007. New anti- ballistic missiles were then added to the system in 2014. These missiles are also slated to be used by the S-500, which also has an unambiguously defined ICBM role.
System Architecture
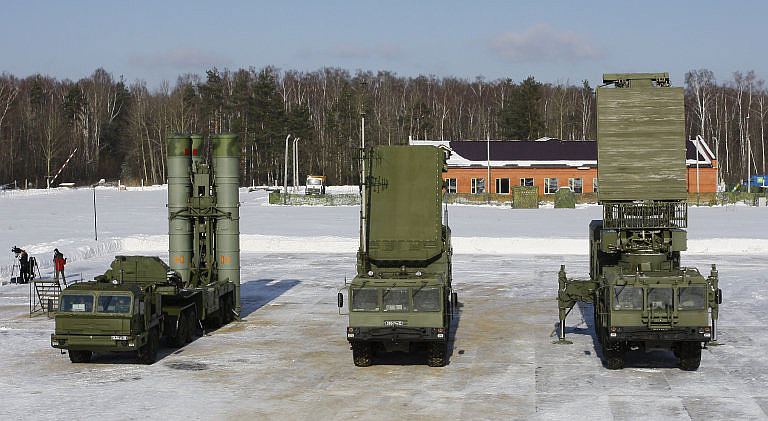
The S-400 Triumf System is designed and equipped to operate in ‘stand- alone’ mode, though it would readily dovetail into an Integrated Air Defence System, incorporating all sensors, shooters and communication links. The LR SAM system has various missiles to cover the entire range spectrum upto 400 km, with the capability to detect and destroy targets flying at altitudes from 100m to 30 km. In the configuration chosen by India, in addition to the radars, each S-400 regiment will consist of eight launchers with two batteries. The system will operate under the Air Defence Command. The system components are elucidated below:-
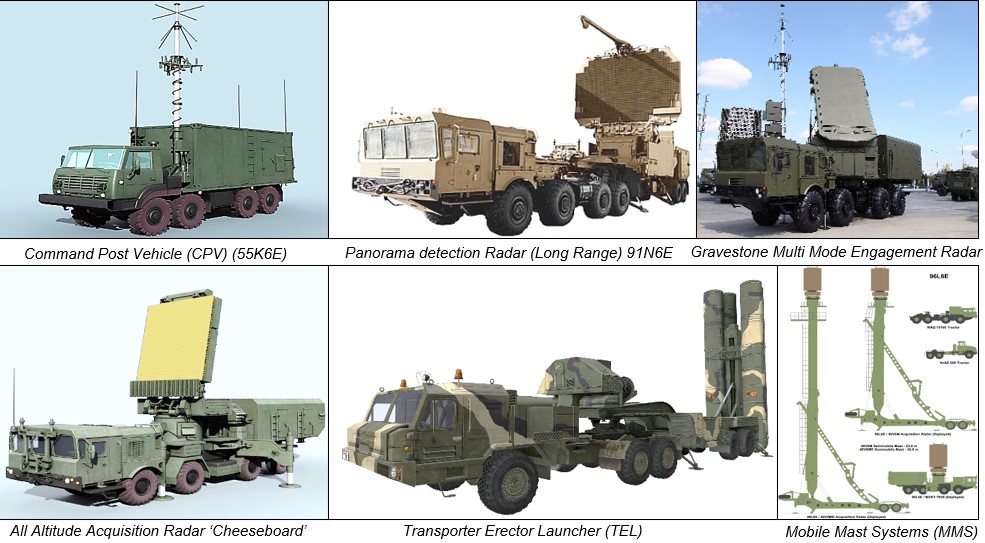
Image Courtsey: metavr.com /ausairpower.net/globalsecurity.org
- Command Post Vehicle (CPV) (55K6E). The S-400 system components are organised around the 306KE Battle Management System, which can coordinate the operation of upto eight missile units. The 55K6E is a command vehicle based on an upgraded version of the Ural chassis. The CPV controls all functions of surveillance, target acquisition, designation, tracking and engagement.
- Panoramic Detection Radar 91N6E (Long Range Surveillance Radar). This panoramic radar detection system has a maximum range of 600 km. The radar is meant to identify, acquire and track aerial and ballistic targets. The system is equipped with an ECCM suite to operate in an adversary initiated intense EW and jamming environment. This radar also has a stipulated targeting range of 150 km against stealth targets.
- ‘Gravestone’ Multi Mode Engagement Radar 92N6E. This is a multi functional radar with a maximum range of 400 km. It can track 100 targets in track-while-scan mode . The radar will automatically prioritise targets, compute Launch Acceptable Regions for missile launches, launch missiles and provide midcourse guidance commands to missiles while tracking the target and missile. The radar is equipped with an IFF capability and an ECCM suite.
- 96L6E ‘Cheeseboard’ All Altitude Acquisition Radar. This is an optional 3D Early Warning and Acquisition Radar which can acquire targets over all altitudes. It was developed to replace the S-Band 36D6 ‘Tin Shield’ medium and high altitude acquisition radar, and the S-Band 76N6 ‘Clam Shell’ low altitude acquisition radar. The radar takes 5 minutes to deploy and is scaled to a missile battery.
- Fire Units. The individual fire units in the battery are designated as 98Zh6E, and comprise a single 92N6E Grave Stone Radar and a group of subordinate Transporter Erector Launchers (TEL). Each battery unit will have eight TELs. Deployment time varies from 3 to 15 minutes.
- TEL. The 5P85TE2 is a self-propelled TEL (Transporter Erector Launcher) mounted on a 8×8 MAZ/ BAZ truck chassis (the 5P85SE2 trailer launcher is also available). Each TEL is configured with four missile tubes.
- Mobile Mast Systems (MMS). The 40V6M/ MD MMS comes configured for the Cheeseboard Radar. These masts are trailor mounted and mount the radar head, thereby functioning to overcome line of sight constraints while tracking low altitude targets.
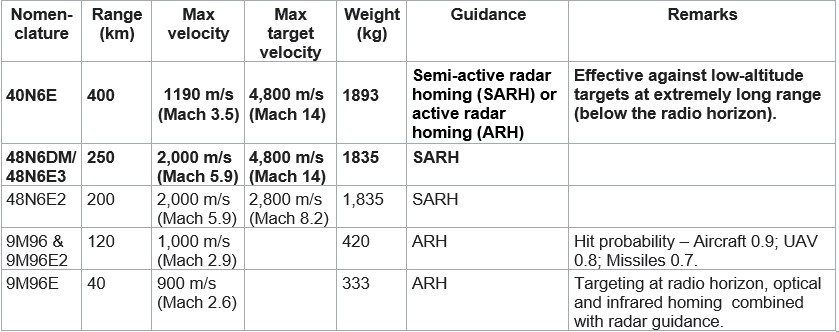
- Missiles. The S-400 System fields four new missile types, in addition to the erstwhile variants. India is likely to purchase only the 250 km-range 48N6 and the 400 km-range 40N6E and is likely to rely on the AKASH and Barak MR/ LR SAM AD Systems for engaging targets at lesser ranges. The salient characteristics of the missile variants are tabulated below:-
- Logistics Maintenance and Support System (LMSS). The LMSS is configured with missile storage, test and maintenance facility. These would include the Loader Vehicle mounted on a 8×8 Ural chassis, if requisitioned.
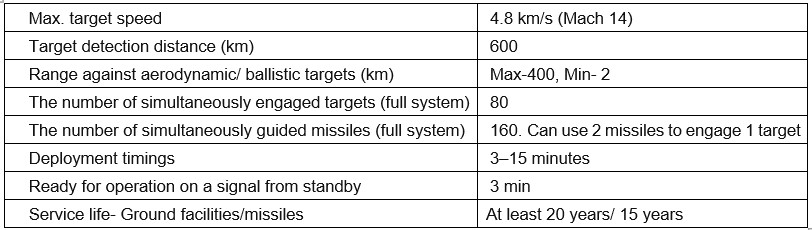
Major Characteristics
The salient characteristics of the S-400 System are tabulated below:-
Comparison With Other AD Systems
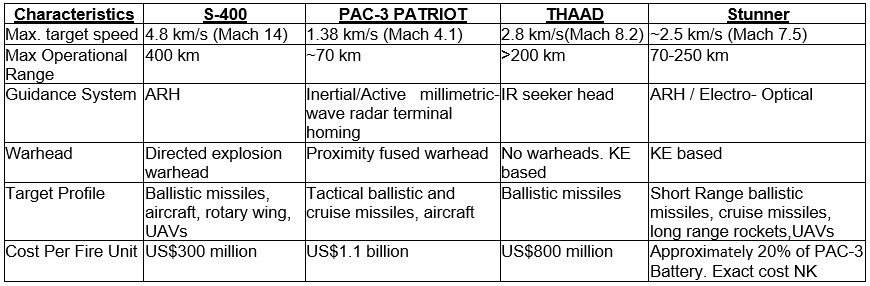
Comparison of the S-400 System with other leading AD systems are elucidated/ tabulated below:-
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defence System (THAAD). The THAAD System of the US is purely an anti- ballistic missile system with ‘hit- to- kill’ interception designed to engage and neutralise short, medium and long range ballistic missiles at very high altitudes (40-50 km), whereas the operational altitude of 30 km for S-400 makes it relevant against missiles as well as fighter aircraft.
- PAC-3 Patriot System. The Patriot System of the US provides medium range air and missile defence over a limited geographical area. The Patriot System can track/ engage 125/ 36 targets simultaneously compared to 160/72 targets by the S-400. Deployment timings for the Patriot System are comparatively greater (upto 25 minutes). No stated stealth detection capability is known to exist with the Patriot System.
- Stunner Missile Interceptor System (SMIS). The SMIS is a two stage interceptor missile system developed to intercept short range ballistic missiles, cruise missiles, long range rockets and UAVs. The SMIS forms part of the David’s Sling Weapon System (DSWS), jointly developed by US and Israel. The DSWS also integrates the Iron Dome AD System and Arrow 2 AD System. The system uses direct ‘hit-to-kill’ technology akin to the THAAD AD System.
Source: defenseworld.net
India And The S-400 Triumf System
India and Russia signed a Government to Government agreement during the BRICS Summit in October 2016 for supply of five S- 400 Regiments. The final signing of the US $ 5.4 Billion deal incurred delays due to the threat of US sanctions under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA), imposed against Russia, Iran and North Korea in July 2017, with an aim to prevent trade partners of the US including India from entering into bilateral contracts with these countries. The threat of US sanctions was further spurred on by the fear that India would seek to establish an Anti-Access Area Denial (A2AD) umbrella over the subcontinent. Another reason for this threat was probably that India chose the Russian S-400 System over the US Origin PAC-3 Patriot and THAAD Systems. The deal was finally inked on 05 October 2018, with India ignoring the threat of US sanctions.
India is scheduled to receive the first consignment of the S-400 System in December 2021. Personnel of Indian Armed forces, with a major Indian Air Force contingent, are already deployed in Russia for training/ facilitation since January 2021.The first Regiment is likely to be delivered/operationalized by April 2022, the second by mid-2022 and the balance three by 2023. Deployment is likely to see three Units on the Western Front and two Units for Eastern Ladakh and the rest of the Northern Borders.
Conclusion
The acquisition of the S-400 Triumf AD System will greatly enhance and correct the imbalance in India’s AD capabilities, to cover the entire gamut of aerial threats. This capability was otherwise due to be only incrementally enhanced from a mere 40 km to a modest 70-100 km, with the induction of the Barak AD Missile System, a joint Indo- Israel venture. Mitigation of such aerial threats would afford imperative freedom of manoeuver to components of the three Services over all three domains, to successfully defend our homeland from external aggression.
*********************************************************************************************************************************
Author

Brig Arvind Dhananjayan (Retd) has commanded an operational Brigade and has been Brigadier- in- charge Administration in a premier training facility. He has had exposure abroad on deputation to Botswana, Southern Africa as member of an Indian Army Training Team and has had extensive exposure in mentoring of Defence Forces overseas. He possesses vast instructional experience, imparting instructions in both technical aspects and tactical application of weapon systems.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the views of Chanakya Forum. All information provided in this article including timeliness, completeness, accuracy, suitability or validity of information referenced therein, is the sole responsibility of the author. www.chanakyaforum.com does not assume any responsibility for the same.
Chanakya Forum is now on . Click here to join our channel (@ChanakyaForum) and stay updated with the latest headlines and articles.
Important
We work round the clock to bring you the finest articles and updates from around the world. There is a team that works tirelessly to ensure that you have a seamless reading experience. But all this costs money. Please support us so that we keep doing what we do best. Happy Reading
Support Us



















POST COMMENTS (10)
Military Contours Of The Russo-Ukraine War - Chanakya Forum
Subhash Sengar
Prashant Singh
amresh
SHIVAM KUMAR THAKUR
Lush C
Ajay Shankar
maisnam Gyanchand luwang
shalin
Rahul