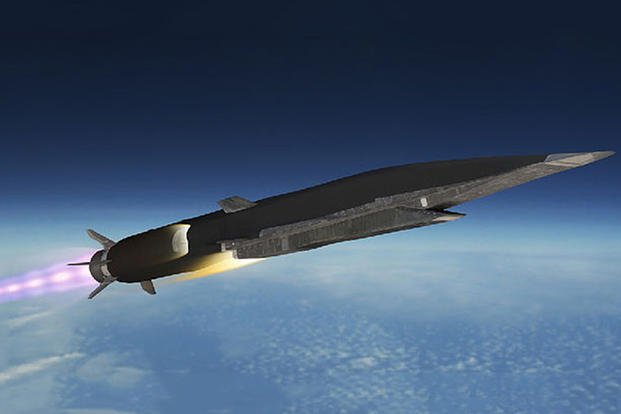

Hypersonic Missiles With Heat-Seeking Technology

The confrontation between Ukraine and Russia is not showing any signs of a ceasefire or end to hostilities. Russia has used its Kh-47M2 Kinzhal hypersonic missile against multiple targets of importance. It consistently enhances its hypersonic prowess, bringing about a new era of extremely fast and lethal conflict.[i]
Not only China, the United States and Russia have invested heavily in hypersonic missiles. Apart from the three military powers, on January 5, 2022, North Korea claimed that it successfully conducted its first significant weapons test of 2022. On January 11, 2022, North Korea conducted its second hypersonic missile test at an undisclosed location, according to state media.[ii]
After orbital bombing systems that are launched from space, which the Chinese were suspected to have built, the new flavour military technology is the hypersonic missile or glide vehicle. Hypersonic missiles travel at hypersonic speeds, or more than five times the speed of sound, like most ballistic missiles. Their main strength is their ability to manoeuvre and fly on lower trajectories than conventional ballistic missiles, which makes them more challenging to track and shoot down.[iii]
IR emissions are frequently depicted in “Green & White” film clips. The term “heat-seekers” is used to describe infrared-seeking systems. They focus on the target’s electronic signature as it is being emitted. The first of these successful missiles were dubbed “Close Combat Missiles (CCMs)”. In the 1950s, the US Navy made use of CCMs. Russia, China, and the United States were evaluating the potential of heating-seeking.
Hypersonic Weapons Development
The United States, China, Russia, and North Korea are testing hypersonic missiles to ensure a high kill probability. Compared to ballistic missiles, these missiles fly closer to their targets while flying at a lower height. In addition, these missiles are built to quickly reach speeds greater than five times the speed of sound.
Many new hypersonic weapons were being developed, according to Putin’s announcement in 2018. From a submarine, Russia fired the Zircon, a hypersonic missile. The Zircon hypersonic missile from Russia has a range of 621 miles and a speed of 9,800 mph. Since the end of 2019, Russia has been using Avangard missiles with a top speed of 27 Mach which have hypersonic nuclear capabilities.
The US Navy, Army, and Air Force are working on various hypersonic weapon programmes. These initiatives are all ongoing. Due to the high level of confidentiality enforced by the USA, many details are not accessible in the public domain. Yet, the initiatives that are now in existence are for the creation of conventional, high-altitude hypersonic weapons.
In December 2022, Chinese scientists asserted to have developed the next generation of heat-seeking hypersonic missiles. China has already demonstrated its capability to launch hypersonic missiles while testing of a hypersonic glide vehicle (HGV), which circled the globe but missed its target by a few kilometres.
According to specific sources, China is currently one step ahead of the US in the race to develop hypersonic weapons. Chinese researchers assert that the new approach using heat seeking technology for hypersonic missiles will simplify procedures to home onto targets. Infrared (IR) emissions from a target is utilised to track and follow it.
Indian Hypersonic Plans
India is one of the few nations developing hypersonic weapons, according to a report by the US Congressional Research Service (CRS). The US, Russia, and China are thought to have the most sophisticated hypersonic weapons programmes, but several other nations, including Australia, India, France, Germany, and Japan, are also working to develop this technology.[iv]
India has been working on the development of Hypersonic missiles for a few years. Defence Minister Rajnath Singh, in a Seminar organised by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in mid-Dec 21 has asked scientists to work towards developing hypersonic missile technology. The DRDO already completed three tests in 2019, 2020, and 2021. The Hypersonic Technology Demonstrator Vehicle (HSTDV) project demonstrated its hypersonic air-breathing scramjet technology. A scramjet engine, also known as a supersonic-combustion ramjet, can impart extremely high speeds to missiles. A scramjet engine can travel between 15 and 20 kilometres above the ground.[v]
Countering Hypersonic Heat-Seeking Missiles
Passive homing missiles are classified as ‘Fire & Forget’ Missiles, but for shorter ranges. Heat seekers pose a higher degree of difficulty in countering it. Passive- homing Missiles with smart technology can’t be jammed. But they can be diverted or fooled by high-intensity heat sources. These IR weapons can be countered by diverting them from their trajectories. Directional IR countermeasures, Chaffs and lasers that disrupt their tracking are the conventional defence against heat seeking weapons.
Chaff is a critical defence technology used to protect targets from hostile heat seekers. The importance of this technology lay in the fact that very less quantity of chaff material deployed in the air act as a decoy to deflect enemy IR missiles to ensure the safety of the fighter aircraft.
The DRDO team has significantly focused on Heat Seekers in the last three years. The development of Hypersonic Heat Seeking systems is still to be meaningfully structured. Necessary R&D will enable the designing of the required techniques. It will take time for all countries to develop an effective counter for Hypersonic heat seeking approaches as vital parameters and specifications need to be discovered.
DRDO has developed an advanced Chaff technology to safeguard the fighter aircraft of the Indian Air Force against hostile IR-based threats. “The IAF has started the process of induction of this technology after the completion of successful user trials,” a DRDO statement said. Defence Laboratory, Jodhpur, developed the advanced Chaff material and chaff cartridge-118/I in collaboration with High Energy Materials Research Laboratory (HEMRL), Pune, meeting the current requirements of the IAF. “The technology has been given to the industry for production in large quantities to meet the annual rolling requirement of the IAF,” it stated.[vi]
It would be crucial for deterrence and operational capabilities for India to develop and construct its arsenal of hypersonic weapons. Advanced technological research involving Directed Energy Weapons (DEW) and non-kinetic weapons is in progress. However, keeping the complexities of Heat seeking guidance systems and the long-range at low-level attack dynamics merits observing the future trials and deployment philosophy to develop effective counter systems.
*******************************************************************************************************
[i] “China far ahead in hypersonic platforms research: Why India needs to step up fast”, FirstPost, January 11, 2023, https://www.firstpost.com/opinion/china-far-ahead-in-hypersonic-platforms-research-why-india-needs-to-step-up-fast-11966732.html. Accessed on March 18, 2023.
[ii] Josh Smith, “N.Korea’s ‘hypersonic missile’ tests raise military stakes in Asia”, Reuters, January 14, 2022, https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/nkoreas-hypersonic-missile-tests-raise-military-stakes-asia-2022-01-14/. Accessed on March 18, 2023.
[iii] Ibid (Reuter).
[iv] “ India Plans Testing of Hypersonic Glide Vehicle in Early January 2023?”, Raksha Anirveda, December 29, 2022, https://raksha-anirveda.com/india-plans-testing-of-hypersonic-glide-vehicle-in-early-january-2023/. Accessed on March 18, 2023.
[v] “India 4th in world with ability to develop Mach 6 missiles”, The Pioneer, 28 January 2023, https://www.dailypioneer.com/2023/page1/india-4th-in-world-with-ability-to-develop-mach-6-missiles.html. Accessed on March 18, 2023.
[vi] “DRDO develops Chaff technology to safeguard fighter jets”, The Hindu, August 19, 2021. https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/drdo-develops-chaff-technology-to-safeguard-fighter-jets/article35993167.ece. Accessed on March 20, 2023.
Disclaimer
The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the views of Chanakya Forum. All information provided in this article including timeliness, completeness, accuracy, suitability or validity of information referenced therein, is the sole responsibility of the author. www.chanakyaforum.com does not assume any responsibility for the same.
Chanakya Forum is now on . Click here to join our channel (@ChanakyaForum) and stay updated with the latest headlines and articles.
Important
We work round the clock to bring you the finest articles and updates from around the world. There is a team that works tirelessly to ensure that you have a seamless reading experience. But all this costs money. Please support us so that we keep doing what we do best. Happy Reading
Support Us




















POST COMMENTS (0)